Bitcoin, difficulty at 129T: hashprice at $60/PH/s and tariffs at 57.6% challenge the miners

Bitcoin’s mining difficulty has climbed to an unprecedented peak of approximately 129 trillion, as reported in August 2025. Simultaneously, the average hashprice hovers near $60/PH/s (Hashrate Index estimates), while U.S. importers of mining hardware confront tariffs as steep as 57.6% on ASIC equipment. These factors are squeezing profit margins, compelling industry players to reassess operational approaches.
Observations from corporate announcements, regulatory filings, and sector analyses up to August 2025 reveal that numerous mining enterprises have adjusted their investment timelines and equipment acquisition strategies. Analysts suggest that mounting tariffs and historic difficulty levels may lead to reduced ASIC purchases and a heightened emphasis on efficiency. These insights align with publicly available data and third-party research within the industry.
Summary
- 129T Bitcoin Difficulty: implications and background
- $60/PH/s Hashprice: strained profitability
- Falling transaction fees: under 1% of block rewards in July 2025
- 57.6% ASIC tariffs: effects on capital expenditure and logistics
- Real-world tariff consequences
- 2025 Outlook: breakeven thresholds, industry consolidation, and challenges
- Miners’ adaptations: operational efficiency, risk management, and agility
- Market repercussions: scenarios and outcomes
- Further analysis
- Recap
Bitcoin Difficulty at 129T: implications and background
Difficulty measures the computational effort required to validate new blocks, adjusting upward as global hashrate expands to maintain a ~10-minute block interval. The 129T milestone underscores advancements in hardware efficiency and the scaling of large mining facilities, directly influencing per-BTC production costs.
Operationally, heightened difficulty reduces the statistical likelihood of solving a block. With BTC prices static, revenue per unit of computing power inevitably declines.
Hashprice at $60/PH/s: strained profitability
Hashprice, measuring daily earnings per computational unit, sits near $60/PH/s amid record difficulty, signaling tighter margins compared to prior market cycles.
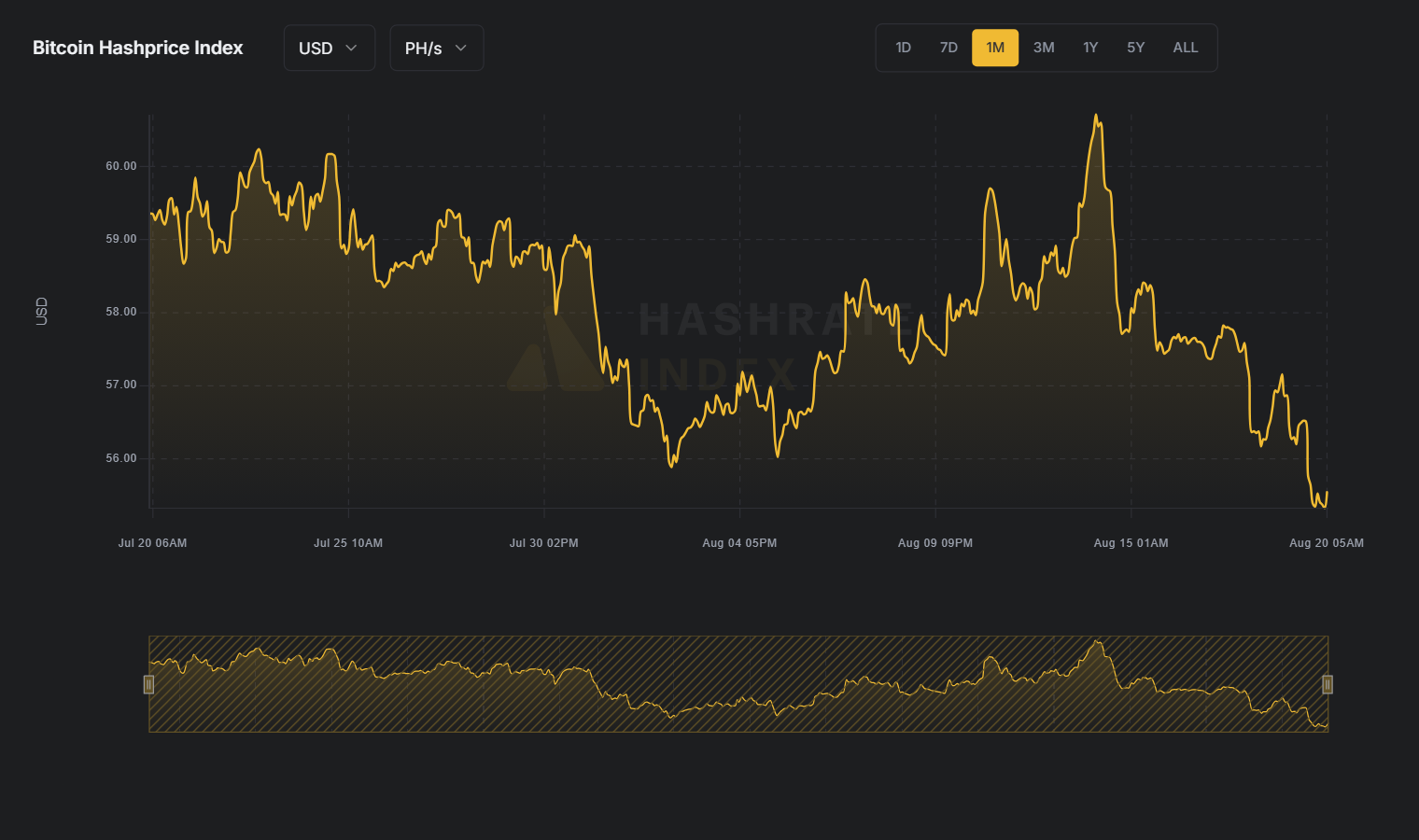
Bitcoin miner profitability plummets following Trump-era tariffs. Source: Hashrate Index
This pressure disproportionately affects operations with elevated energy costs or outdated equipment (higher W/TH ratios). Many miners now face raised breakeven thresholds, amplifying vulnerability to BTC price swings.
Falling transaction fees: under 1% of block rewards in July 2025
During July 2025, transaction fees contributed less than 1% to block rewards. Consequently, miners’ income relies predominantly on the fixed 3.125 BTC subsidy (post-halving), increasing exposure to difficulty adjustments and BTC valuation shifts.
Depressed fees heighten revenue volatility, where minor fluctuations in price or network activity can substantially affect financial performance.
57.6% ASIC tariffs: effects on capital expenditure and logistics
Recent U.S. trade policies impose 57.6% tariffs on imported mining hardware, inflating capital costs for equipment upgrades and expansions. Delays in supply chains and increased working capital requirements have been observed.
CleanSpark disclosed potential liabilities nearing $185 million, while Iris Energy faces claims exceeding $100 million, both firms contesting U.S. Customs assessments.
Real-world tariff consequences
- Higher per-unit expenses for ASICs and components
- Prolonged delivery periods and expanded inventories for risk mitigation
- Revised expansion strategies prioritizing energy-efficient hardware
- Disputed liabilities and financial reporting ambiguities
2025 Outlook: breakeven thresholds, industry consolidation, and challenges
Miners’ 2025 profitability hinges on energy pricing, network difficulty, and hashrate valuations. With record difficulty and minimal fees, the sector may witness mergers, delayed ASIC deployments, and migration to energy-rich regions. Potential difficulty reductions or hashprice rebounds could provide temporary relief, though structural challenges—tariffs and energy costs—demand strategic overhauls.
Miners’ adaptations: operational efficiency, risk management, and agility
- Energy management: hardware modernization, liquid cooling, grid-balancing initiatives
- Supply chain adjustments: vendor diversification, regional sourcing, contract revisions
- Financial hedging: BTC futures, hashrate-linked derivatives (e.g., Hashrate Index tools)
- Sustainable practices: renewable energy integration, stranded power utilization
Market repercussions: scenarios and outcomes
Margin compression may drive attrition among high-cost operators, benefiting efficient competitors. BTC price surges or difficulty dips could boost margins, though tariff and energy uncertainties persist.
Further analysis
- Bitcoin mining mechanics: hashrate, difficulty, rewards explained
- BTC halving: implications for miners and markets
- Current BTC valuation drivers
Recap
Key points: 129T difficulty, ~$60/PH/s hashprice, <1% fee share in July 2025, and 57.6% ASIC tariffs in the U.S. Miners face ongoing pressures in 2025, balancing capital costs against efficiency demands. Sector stability remains tied to BTC valuations, energy markets, and policy developments.
Disclosure: Data sourced from Hashrate Index, Blockchain.com Charts, and Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index.
Source: cryptonews.net



