Bitcoin Mining Difficulty Reaches ATH, But Expected to Decline in August

Bitcoin (BTC) mining difficulty hit a record high of 127.6 trillion this week, but is expected to drop during the next difficulty adjustment on August 9.
According to CoinWarz, mining difficulty is expected to decrease by around 3% to 123.7 trillion in the next adjustment cycle, while the average block time is currently around 10 minutes and 20 seconds.
Data from CryptoQuant indicates that mining difficulty declined in June, falling sharply at the end of the month and in the first two weeks of July, when it reached 116.9 trillion. However, difficulty began its long-term rise again in the second half of July.
Bitcoin mining difficulty and the network hashrate (the total computing power that secures the network) are critical factors influencing miner profitability and maintaining a high Bitcoin stock-to-flow ratio, which protects the BTC price from oversupply.
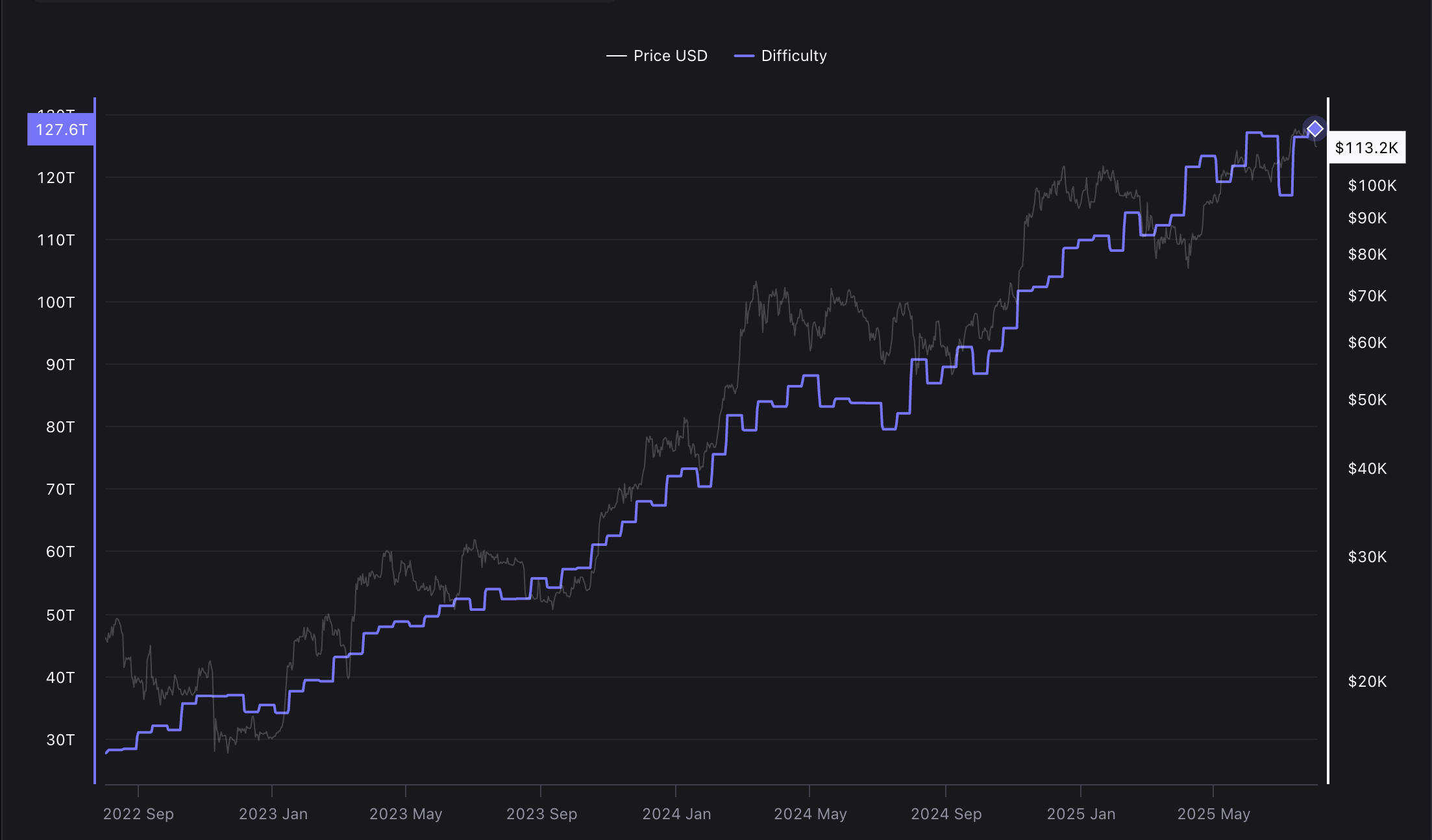 Bitcoin mining difficulty has reached a new all-time high and continues to increase gradually. Source: CryptoQuant
Bitcoin mining difficulty has reached a new all-time high and continues to increase gradually. Source: CryptoQuant
Related: Solo Bitcoin Miner Receives $373,000 Block Reward
Bitcoin Difficulty Adjustment and Stock to Flow Ratio
The stock to flow ratio shows the total available supply of a financial asset or commodity compared to newly created supply added by miners or producers.
The higher the ratio, the more resistant the asset or commodity is to price changes caused by excess supply; the lower the ratio, the more susceptible the asset or commodity is to new supply.
This ratio partly explains why silver has been displaced by gold. Silver has a lower stock-to-flow ratio than gold. Higher silver prices attract miners and producers to expand supply, which floods the market with new silver and drives prices down.
Bitcoin has a higher stock-to-flow ratio than gold, with about 94% of the 21 million BTC already mined and circulating in the markets. In contrast, gold has no hard supply cap and an inflation rate of about 2% per year.
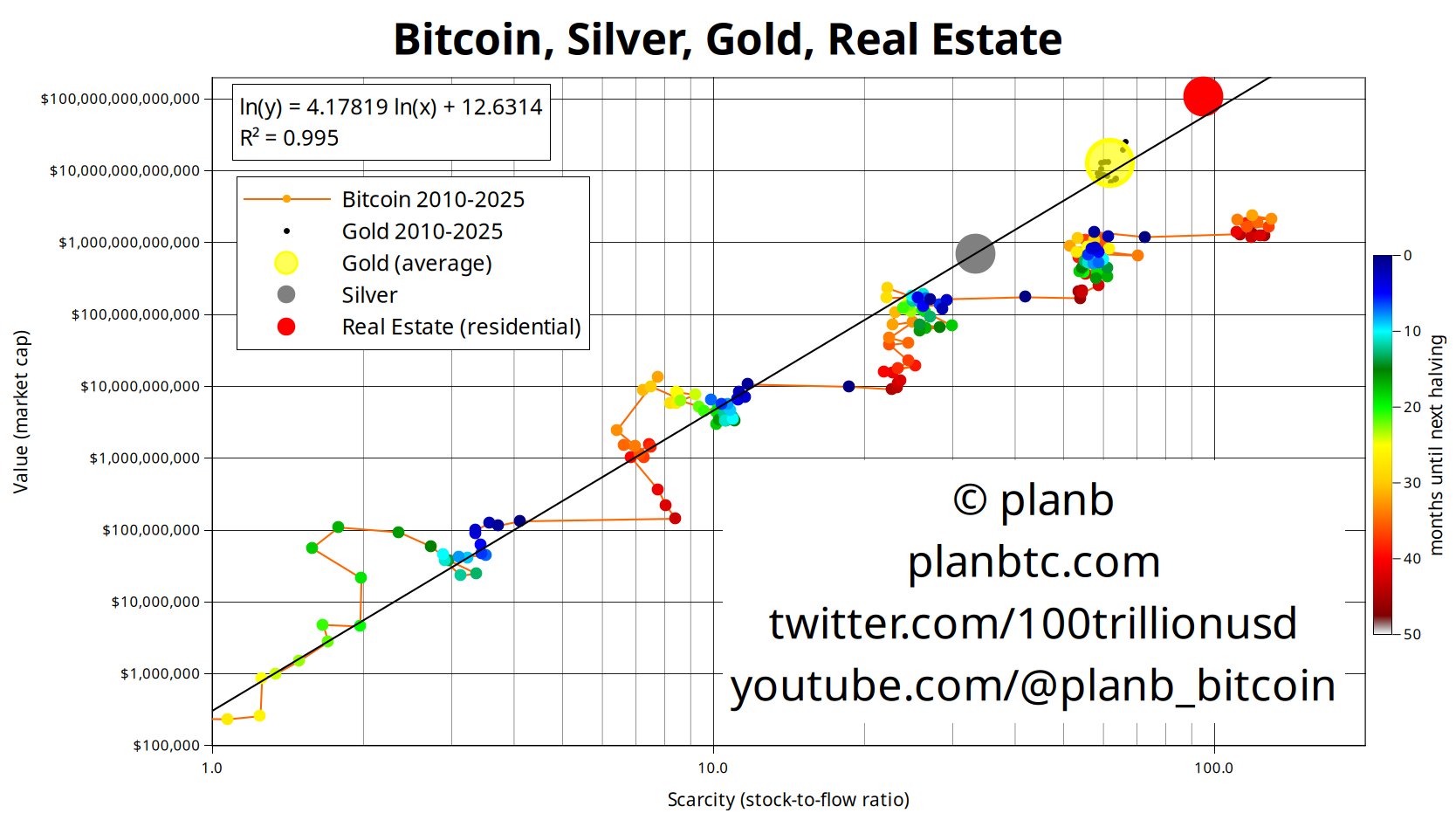 Comparing Bitcoin's stock-to-flow ratio to gold, silver, and residential real estate. Source: PlanB
Comparing Bitcoin's stock-to-flow ratio to gold, silver, and residential real estate. Source: PlanB
“Gold’s scarcity, the stock-to-flow ratio, is about 60. Bitcoin’s scarcity is about 120. That means Bitcoin is twice as scarce as gold,” says PlanB, the author of the stock-to-flow model for Bitcoin’s price analysis.
The difficulty adjustment makes Bitcoin's price less sensitive to mining volume, which remains proportional to the total computing power used by miners.
Difficulty adjustment prevents oversupply and subsequent price declines due to new supply entering the market in large quantities over a short period of time.
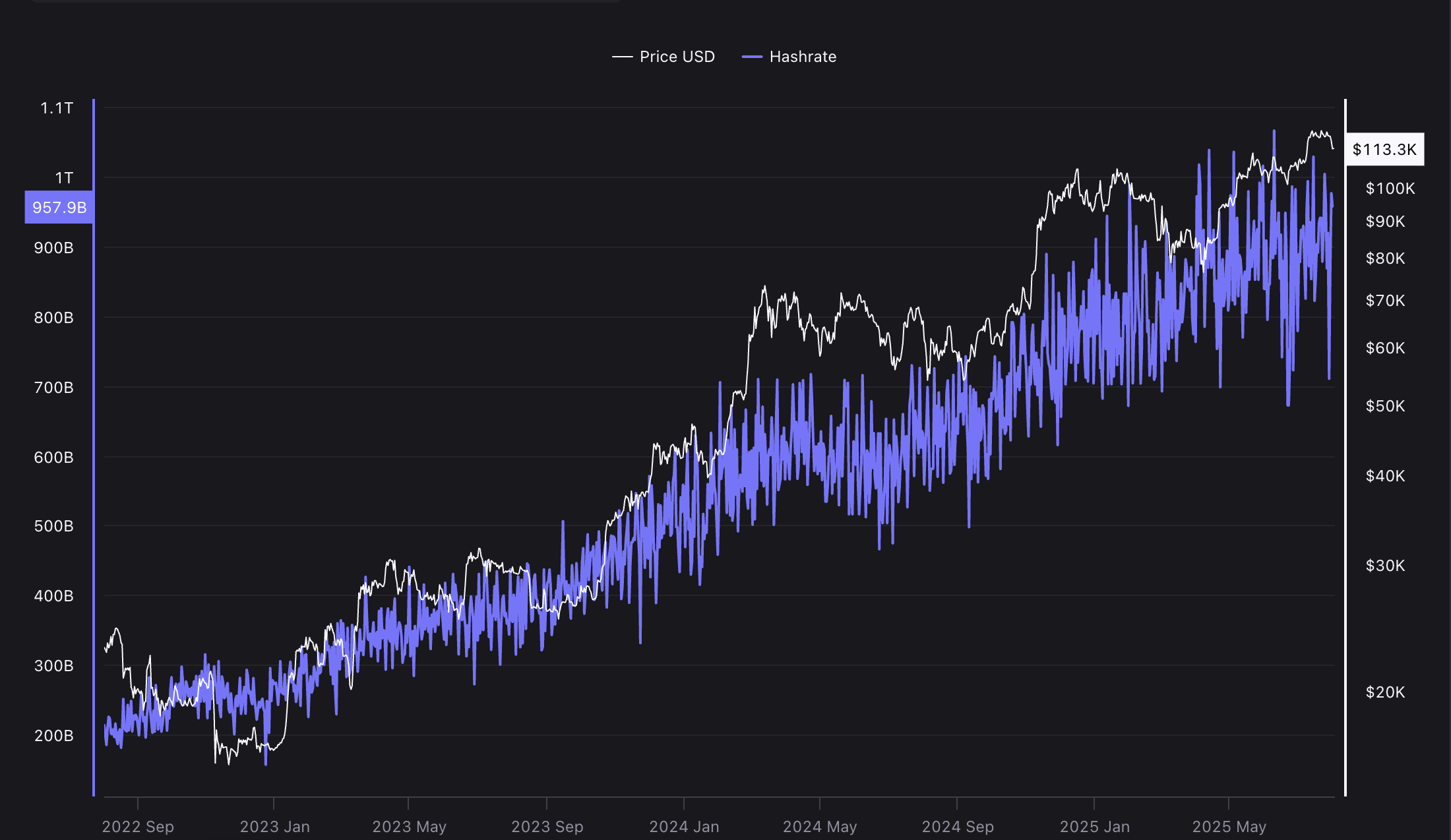 The Bitcoin network hashrate represents the total computing power used to secure the network. Source: CryptoQuant
The Bitcoin network hashrate represents the total computing power used to secure the network. Source: CryptoQuant
As the computing power used to secure the Bitcoin network increases, its difficulty increases to accommodate the new resources and keep block production as close as possible to the 10-minute target set by the protocol.
Otherwise, if the computing power decreases, the network difficulty drops to ensure a constant rate of new blocks are mined within about 10 minutes.
Journal: Bitcoin vs. the Quantum Computer Threat: Timeline and Solutions (2025–2035)
Source: cryptonews.net



