

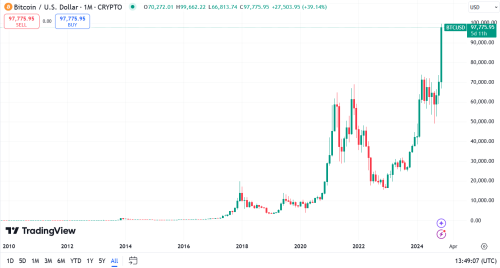
In 2010, Laszlo Hanyecz, an early Bitcoin enthusiast, used 10,000 Bitcoins to buy two pizzas. By 2024, a single bitcoin was worth nearly $100,000, making Bitcoin (BTC) the most expensive crypto. Several other cryptocurrencies trade for hundreds or even thousands of dollars per coin, including some that aren’t mentioned on the nightly news.
The question “What is the most expensive cryptocurrency?” centers on price per coin rather than total market value, the latter of which can be inflated by a large supply. Early success stories like Bitcoin and Ethereum are still among the most expensive crypto assets when measured by price per coin. However, some newer coins and tokens have now joined this elite group of crypto assets.
Let’s review the highest-price crypto coins and what makes them stand out in an ever-growing market of new cryptocurrencies.
The most expensive crypto coins include some familiar names like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and BNB, but a handful of growing projects also join this select group. One, Tether Gold, even acts as a blockchain proxy for a real-world asset (gold). Let’s compare the most expensive cryptocurrencies.

BTC -2.58%

YFI -5.64%

ETH -3.58%

XAUT +0.01%

MKR -7.98%

BNB -0.90%

TAO +0.00%

BCH -3.42%
The most expensive cryptocurrencies each have differing backstories, but they all owe a debt to Bitcoin, which is credited with being the first decentralized blockchain. Although Bitcoin paved the way for newer projects, these new projects brought additional functionality to blockchains. The highest-priced crypto coins represent a wide gamut of roles within the crypto ecosystem, ranging from fuel tokens to governance tokens to cryptocurrencies backed by real-world assets.

- Price: $104,291.00
- Market Cap: $2.06T
- Supply: 19.79M
Bitcoin was created by an anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. In October 2008, Satoshi published the Bitcoin Whitepaper, and the Bitcoin network went live in January 2009. A small group of early adopters helped the fledgling network find its footing, and the value of a single bitcoin wasn’t yet known.
The infamous purchase of two pizzas for 10,000 bitcoins in 2010 put the speculative value at a fraction of a penny per bitcoin.
By March 2010, Bitcoinmarket, the first crypto exchange, launched. This exchange, along with the addition of countless new exchanges that followed, helped Bitcoin reach a wider market, allowing price discovery over time through worldwide trading.
Over the years, Bitcoin has risen in value to the six-figure range, and many expect this “digital gold” to reach much higher prices. Several characteristics of Bitcoin help make it crypto’s most valuable asset.
The protocol uses proof of work to secure transactions on the blockchain, and a worldwide network of miners works around the clock to mine the next block while also securing previous blocks.
Decentralization also makes Bitcoin attractive to investors. Although a core group of developers maintains the code and rolls out improvements, the network itself acts as a voting body, deciding which version of Bitcoin’s software will prevail by choosing which version to run on individual nodes.
Although there are newer coins that promise similar features and security, none have the worldwide adoption Bitcoin enjoys.
24h7d30d1yAll time Bitcoin Pros & Cons
Pros
- Worldwide adoption
- Available through exchange-traded funds
- Unrivaled network security
- Worldwide decentralized network
- Limited supply (21 million bitcoins)
Cons
- Price volatility
- High energy usage
- Limited acceptance for transactions
2. Yearn Finance ($10,040.29)

- Price: $10,040.29
- Market Cap: $335.67M
- Supply: 33.43K
Yearn Finance is a yield aggregation protocol. Decentralized finance (DeFi) offers a new way to earn yields and put crypto assets to work. However, these opportunities can be difficult to find, and each has its own UI, making navigation challenging. Yearn Finance brings some of the best yield opportunities together in one place, allowing investors to interact with protocols using a familiar interface.
The Yearn Finance token, while available on crypto exchanges, is also awarded to platform users. However, unlike many incentive tokens, the supply is capped. Only 36,666 tokens exist, making Yearn Finance one of the smallest supplies in all of crypto.
The Yearn Finance token acts as both an incentive to use the platform and a governance token, with tokens used to vote on platform proposals, called Yearn Improvement Proposals (YIPs). Other governance roles for the token include Yearn Delegation Proposals (YDPs) and Yearn Signaling Proposals (YSPs).
24h7d30d1yAll time YFI Pros & Cons
Pros
- Low supply
- Available on top crypto exchanges
- Voting rights for a leading DeFi platform
Cons
- Price volatility
- Limited chains supported
- A limited number of holders
3. Ethereum ($3,868.04)
Bitcoin was created by an anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. In October 2008, Satoshi published the Bitcoin Whitepaper, and the Bitcoin network went live in January 2009. A small group of early adopters helped the fledgling network find its footing, and the value of a single bitcoin wasn’t yet known.
The infamous purchase of two pizzas for 10,000 bitcoins in 2010 put the speculative value at a fraction of a penny per bitcoin.
By March 2010, Bitcoinmarket, the first crypto exchange, launched. This exchange, along with the addition of countless new exchanges that followed, helped Bitcoin reach a wider market, allowing price discovery over time through worldwide trading.
Over the years, Bitcoin has risen in value to the six-figure range, and many expect this “digital gold” to reach much higher prices. Several characteristics of Bitcoin help make it crypto’s most valuable asset.
The protocol uses proof of work to secure transactions on the blockchain, and a worldwide network of miners works around the clock to mine the next block while also securing previous blocks.
Decentralization also makes Bitcoin attractive to investors. Although a core group of developers maintains the code and rolls out improvements, the network itself acts as a voting body, deciding which version of Bitcoin’s software will prevail by choosing which version to run on individual nodes.
Although there are newer coins that promise similar features and security, none have the worldwide adoption Bitcoin enjoys.
24h7d30d1yAll time Bitcoin Pros & Cons
Pros
- Worldwide adoption
- Available through exchange-traded funds
- Unrivaled network security
- Worldwide decentralized network
- Limited supply (21 million bitcoins)
Cons
- Price volatility
- High energy usage
- Limited acceptance for transactions
2. Yearn Finance ($10,040.29)
Bitcoin was created by an anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. In October 2008, Satoshi published the Bitcoin Whitepaper, and the Bitcoin network went live in January 2009. A small group of early adopters helped the fledgling network find its footing, and the value of a single bitcoin wasn’t yet known.
The infamous purchase of two pizzas for 10,000 bitcoins in 2010 put the speculative value at a fraction of a penny per bitcoin.
By March 2010, Bitcoinmarket, the first crypto exchange, launched. This exchange, along with the addition of countless new exchanges that followed, helped Bitcoin reach a wider market, allowing price discovery over time through worldwide trading.
Over the years, Bitcoin has risen in value to the six-figure range, and many expect this “digital gold” to reach much higher prices. Several characteristics of Bitcoin help make it crypto’s most valuable asset.
The protocol uses proof of work to secure transactions on the blockchain, and a worldwide network of miners works around the clock to mine the next block while also securing previous blocks.
Decentralization also makes Bitcoin attractive to investors. Although a core group of developers maintains the code and rolls out improvements, the network itself acts as a voting body, deciding which version of Bitcoin’s software will prevail by choosing which version to run on individual nodes.
Although there are newer coins that promise similar features and security, none have the worldwide adoption Bitcoin enjoys.
24h7d30d1yAll time Bitcoin Pros & Cons
Pros
Cons

Yearn Finance is a yield aggregation protocol. Decentralized finance (DeFi) offers a new way to earn yields and put crypto assets to work. However, these opportunities can be difficult to find, and each has its own UI, making navigation challenging. Yearn Finance brings some of the best yield opportunities together in one place, allowing investors to interact with protocols using a familiar interface.
The Yearn Finance token, while available on crypto exchanges, is also awarded to platform users. However, unlike many incentive tokens, the supply is capped. Only 36,666 tokens exist, making Yearn Finance one of the smallest supplies in all of crypto.
The Yearn Finance token acts as both an incentive to use the platform and a governance token, with tokens used to vote on platform proposals, called Yearn Improvement Proposals (YIPs). Other governance roles for the token include Yearn Delegation Proposals (YDPs) and Yearn Signaling Proposals (YSPs).
24h7d30d1yAll time YFI Pros & Cons
Pros
Cons

Launched in 2015, the Ethereum protocol is credited with bringing smart contract functionality to blockchains. Although several leading chains also offer smart contracts, Ethereum remains the market share leader with more than $72 billion in total value locked (TVL), including staking, which is the chain’s method for securing the network.
Unlike Bitcoin, which surpassed its 2021 all-time high in 2024, Ethereum has not yet surpassed its previous high, leading many to believe that Ethereum may offer better performance in the future. Similar to Bitcoin, the supply is stable. However, Ethereum uses a different strategy to manage supply. The protocol burns base fees paid for network transactions by sending these fees to an unrecoverable address on the blockchain. At the same time, the protocol mints new tokens as staking rewards. The result has been a slightly deflationary ETH supply since the protocol switched to proof of stake from proof of work in 2022.
Ethereum’s active development, stable supply, and vibrant ecosystem keep ETH in high demand for both investors and those who actively participate in the ETH ecosystem.
24h7d30d1yAll time ETH Pros & Cons
Pros
Cons
Tether made its name in the crypto space with its USDT stablecoin, which tracks the value of the US dollar by backing each token with cash or other reserve assets, such as US treasury bonds. In 2020, the company launched its gold-backed token, Tether Gold (XAUt).
While backed by physical gold, the Tether Gold token offers much better portability than physical gold, allowing users to transfer a gold-backed asset anywhere in the world in seconds. Holders can also travel anywhere in the world with their gold-backed tokens secured by a cryptocurrency wallet.
Since its launch, Tether Gold has become the leading gold-backed crypto token, owing its popularity to the name recognition of Tether’s USDT itself, which launched in 2014.
24h7d30d1yAll time XAUT Pros & Cons
Pros
Cons

Although dollars or other real-world financial instruments back other popular stablecoins, MakerDAO launched its DAI stablecoin in 2014, choosing to back the coin with crypto rather than dollars or bonds. In effect, every DAI token has been borrowed into existence, using a select group of cryptocurrencies as collateral. This overcollateralized structure makes DAI safer than algorithmic stablecoins and more transparent than dollar-backed stablecoins.
The MakerDAO Protocol is at the heart of DAI, with the Maker (MKR) token serving as a governance token for the protocol. MKR holders vote on proposed changes to the protocol and which cryptocurrencies are accepted as collateral to back the DAI stablecoin to ensure parity with the US dollar.
MakerDAO has since rebranded to SKY, which, as part of the conversion, now offers token rewards. DAI stablecoin tokens can be redeemed through the new USDS token, although many external protocols still support DAI.
24h7d30d1yAll time MakerDAO Pros & Cons
Pros
Cons

Originally launched by the Binance exchange as an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain, BNB later became the fuel token for its own smart contract payments network. At launch, BNB, also called Binance Coin at the time, was intended to pay fees on the Binance trading platform. To this day, Binance still offers a discount for fees paid in BNB.
However, the BNB digital currency now also serves as a fuel token for the Binance Smart Chain (BSC), which shares much of its structure with Ethereum, although streamlining the consensus for the network with a smaller number of validators.
Many remain bullish on the BNB token due to the active burning of the token, which reduces supply and potentially boosts prices for BNB. The BNB protocol uses an Auto-Burn mechanism to burn BNB tokens until the supply is reduced to 100 million tokens.
24h7d30d1yAll time BNB Pros & Cons
Pros
Cons

The TAO token acts as a fuel token for Bittensor, a peer-to-peer artificial intelligence market. In effect, Bittensor’s TAO token rewards participants for contributing to the network.
Similar to Bitcoin, TAO has a fixed supply of 21 million tokens. Although fewer than eight million tokens are in circulation, meaning most are yet to reach the market, the fixed maximum supply coupled with the early stages of the AI market makes TAO one of the most expensive crypto tokens.
24h7d30d1yAll time Bittensor Pros & Cons
Pros
Cons

The Bitcoin Cash network began as a hard fork of the Bitcoin network in 2017. The fork came after a debate over scaling. As a result, Bitcoin split into two networks: Bitcoin Cash, which had larger block sizes, and the original Bitcoin network, which retained the smaller block sizes. Both networks had a shared history of transactions up until the fork, then diverged as users chose which network to use.
Like Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash has a maximum supply of 21 million coins. The network also uses proof of work to validate transactions and secure the blockchain. Overall, Bitcoin Cash is faster than Bitcoin and offers comparatively inexpensive transactions. Bitcoin Cash also supports smart contracts through a language called CashScript, which follows a similar syntax to Ethereum’s Solidity programming language.
24h7d30d1yAll time BCH Pros & Cons
Pros
Cons
The most expensive crypto can be a confusing term. However, there’s a distinction between the highest price per token and the highest market capitalization. While Bitcoin takes the lead in both categories, the price per coin is what defines a coin as being the most expensive.
In many cases, supply plays a big role in the price per coin, although demand must also be strong.

Market cap refers to the collective value of all the coins or tokens in circulation, whereas price per coin refers to the price for each coin or token. Which matters more depends on your investment priorities.
For example, if your goal were to own 0.01 bitcoins, that amount wouldn’t be as meaningful if Bitcoin’s market cap was still under $100,000. Now, a single Bitcoin is worth about that amount.
However, market capitalization – and fully diluted market capitalization – are considered more important metrics when assessing an investment from a fundamental perspective. These refer to the value of the circulating supply or the value of the total supply, respectively.
Several factors can contribute to a higher price per coin, with low supply and high demand being the most common. Some coins are also deflationary, meaning the supply shrinks over time, pushing prices higher if demand continues to rise.
The low circulating supply can affect the price per token. However, experienced investors are likely to evaluate the supply that will become available in the future.
An increase in the supply can cause the price per token to fall. This means that investors should consider both the future supply and how long it will take for the additional supply to reach the market. If an additional token release takes years, the circulating supply will grow slowly, allowing time for demand to grow to match the expected supply.
Several of the most expensive crypto coins have fixed or deflationary supplies. BTC, BCH, and TAO all have a maximum supply of 21 million coins. Ethereum and BNB, while not fixed, have been deflationary in recent years due to token burning. This stable or shrinking supply bodes well for the price per coin, assuming demand remains strong.
Growing market demand can cause the price per token to rise even if there is more supply yet to be released. Bittensor’s TAO token provides a good example. Although the maximum supply is 21 million, only 7.4 million tokens are in circulation. Despite the overhanging supply, TAO saw a 5x increase between November of 2023 and November 2024.
Are the most expensive crypto coins too expensive to buy? Not necessarily. Buying an expensive crypto like Bitcoin or Ethereum may be a safer investment than buying a new but unproven coin at a lower price per coin. Let’s look at some of the advantages of buying the most expensive crypto coins.

Often, the highest-price crypto coins or tokens are also those that are further along in their distribution schedule. With Bitcoin nearly 20 million out of a max supply of 21 million bitcoins mined, interest in Bitcoin as an investment has never been higher. Less than 5% of the Bitcoin supply remains to be mined. Bitcoin halving events will cause the remaining bitcoins another 100+ years to be mined in full.
This reduced risk of dilution makes many investors feel more confident in paying more for each coin as demand remains strong.
As with many types of digital assets, a higher price comes as a result of a proven reputation and trust earned over time. When Bitcoin launched, few people understood how it worked or why it might one day have much more value. In effect, a higher price per coin signifies quality for many investors, akin to buying a premium brand rather than a cheaper imitation.
Owning the most expensive cryptocurrencies comes with some downsides as well. Notably, you can expect less dramatic price performance. However, downswings can also be amplified. Let’s take a look at how these market forces affect the highest-price cryptos.
During bull market runs, 20x, 50x, or even 100x success stories abound. However, these types of gains become increasingly unlikely in the short term for the most expensive cryptocurrencies. The stratospheric growth seen with Bitcoin, Ethereum, or BNB in the early days typically subsides, flattening the chart in comparison to early runs.
This flattening of the chart is, in part, a product of the asset’s market capitalization. At a nearly $2 trillion market capitalization, Bitcoin isn’t likely to see a 20x in a year, which would make Bitcoin’s market cap three times larger than the US gross domestic product (GDP).
Higher-priced cryptocurrencies can also see steeper declines when the market turns south. Fewer buyers arrive to rescue the chart because the price seems, well, high. This can lead to a freefall in market prices, much like we saw in late 2021 after Bitcoin fell from a high of $69,000. Despite some attempts at recovery, the freefall didn’t end until BTC fell below $16,000 in late 2022.
What is the most expensive cryptocurrency? It’s still Bitcoin, and BTC will likely remain king of the hill in the foreseeable future. However, a higher cost per coin only tells part of the story. Some of the most expensive cryptocurrencies are costlier per coin because the supply is relatively small relative to the demand. When choosing a cryptocurrency for your portfolio, also consider the market capitalization, how much supply is yet to be released, and price or demand trends.
Bitcoin is the most expensive cryptocurrency. At about $100,000 per Bitcoin is more than ten times more expensive than the next highest-price cryptocurrency.
Buying a more expensive cryptocurrency can be a good investment because the high price signifies that the market sees it as a safer choice. However, when the market changes direction, falls from grace can happen swiftly as buyers begin to doubt the lofty price tag.
Expensive cryptocurrencies aren’t necessarily overvalued. However, they may see less dramatic growth than seen in the earlier days following the project’s launch.
Market capitalization is a better indicator of a crypto’s price point than the price per token. Compare the market cap and the fully diluted market cap to the utility and adoption rates to decide whether a cryptocurrency is undervalued, overpriced, or trading at fair value.
Source: cryptonews.com
Your email address will not be published.
[…] January 2022, the number of cryptocurrencies existing in the market increased by 1 thousand. This implies that each new…
Your writing is like a breath of fresh air in the often stale world of online content. Your unique perspective…
I would like to share my story and express my great gratitude to Maria. My husband Alexander was literally taken…